Usage: Click the Help button at any time to get online help for the settings in the current tab.
This opens a World Wide Browser, such as Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer, and displays information about the settings.
To close the help display, close the browser as you would any other program. For example, in Windows 95, click the X button at the upper right of the window or choose Exit from the File menu.
With some browsers, a new window will open each time you click the Help button. If this happens, simply close each window when you're done with it.
Finding setting descriptions: At the beginning of each help window is a table of contents for the window. To go information about a particular setting, click the hyperlink (the underlined text in most browsers) for that setting in the contents. To return to the contents, use the control in your browser for going back, such as the Back button in Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer 3.0.
Update
Description: Sends configuration settings to the Pipeline.
Usage: Click this button to send the settings shown in the Java-Based Pipeline Configurator to the Pipeline.
These new settings replace the previous settings in the Pipeline. You can use this button at any time; you do not have to enter values for all settings before updating the Pipeline.
Save As
Description: Saves configuration settings in a file.
Usage: Click this to save the settings shown in the Java-Based Pipeline Configurator in a file on your computer.
You then use your operating system's facility for specifying a name and location for the file, such as the Save To dialog box in Windows 95.
You can later open a file in which you've saved settings by clicking the Open a Configuration File button in the first window that appears when you run the Java-Based Pipeline Configurator.
You can use this button at any time; you do not have to enter values for all settings before saving settings.
Open Monitor
Description: Opens the Pipeline Monitor, a program for monitoring the status of the Pipeline unit as well as making and disconnecting ISDN connections manually. You can also use it to view the current status of the ISDN line as well as events that occur during Pipeline operation. For more information about the Pipeline Monitor, see Using the Pipeline Monitor.
Usage: Click this to open the Pipeline Monitor.
Usage: Choose one of the following:
Usage: If the checkbox is checked, the Pipeline rejects incoming calls for which it can find no Connection Profile and no entry on a remote authentication server. If the checkbox is not checked, the Pipeline does not require a Connection Profile or a remote authentication entry. By default, the checkbox is not checked.
If Require Connection Profile is checked, one of the following must be true for each incoming data call for the connection to be made:
Allow Multiple Connections per Profile
Description: This checkbox controls whether multiple incoming callers can share a Connection Profile.
Usage: Check the box to allow multiple incoming calls to share a Connection Profile.
Dependencies: The Pipeline must first authenticate each caller using the caller's name and password. If an incoming call has an IP address that conflicts with the IP address of another caller, the Pipeline rejects the call.
Authentication
Description:
This setting specifies the authentication protocol that the Pipeline uses when receiving and verifying a password for an incoming PPP call.
If you choose PAP, the Pipeline uses this protocol for authentication. The remote device must support PAP.
If you choose CHAP, the Pipeline uses this protocol for authentication. The remote device must support CHAP.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage:
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 65535. If you specify 0 (zero), Pipeline does not enforce a limit; an idle connection stays open indefinitely.
The default setting is 120 seconds.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Choose one of the following:
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
If the caller requests MS-Stac and the profile does not specify MS-Stac compression, the connection seems to come up correctly, but no data is routed. If the profile is configured with MS-Stac and the caller does not acknowledge that compression scheme, the Pipeline attempts to use standard Stac compression. If it cannot use standard Stac compression, it uses no compression at all.
Usage: The default setting is 1524; you should accept this default unless the device at the remote end of the link cannot support it.
If the administrator of the remote network specifies that you must change this value, enter a number between 1 and 1524.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Click the Data Filter button. In the window that appears, select a data filter and then click OK.
If you choose None, the Pipeline forwards all data packets. None is the default.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
LQM is a feature that enables the Pipeline to monitor the quality of a link. LQM counts the number of packets sent across the link and periodically asks the remote end how many packets it has received. Discrepancies are evidence of packet loss and indicate link quality problems.
LQM causes the generation of periodic link quality reports. Both ends of the link exchange these reports.
Usage:
This is the default.
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 600. The default is 600.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 600. The default is 600.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Check the box to enable bridging.
This is unchecked by default.
Dependencies: The effect of the Enable Bridging setting depends upon how you set the Enable IP Routing and Enable IPX Routing settings.
Enable Bridging and Enable IP Routing
Usage: If checked, the Pipeline requests IPX routing.
By default, this is not checked.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Click the SAP Filter button. In the window that appears, select a SAP filter or None and then click OK.
If you select None, all SAP data is included in the service table. None is the default.
Use this feature when you place calls to European or Pacific Rim countries and the complete path cannot distinguish between the Switched-56 and Switched-64 data services. This feature is not required if you are placing calls only within North America.
Usage: Check the box to use only the 56-Kbps portion of a channel.
If the box is not checked, the Pipeline can use 64 Kbps, if available. By default, it is not checked.
The Pipeline uses the historical time period specified by the Sample Time setting as the basis for calculating ALU. It then compares ALU to the amount specified in the Target % setting. When ALU exceeds the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. When ALU falls below the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove the a channel.
MP+ supports Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation.
Usage: Choose one of the following:
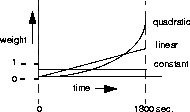
This graph illustrates the effect of each algorithm:

Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
When ALU exceeds the Target % threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel.When ALU falls below the Target % threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel.
The number of seconds you choose for the Sample Time setting depends on your device's traffic patterns. For example, if you want to average spikes with normal traffic flow, you may want the Pipeline to establish a longer historical time period. If, on the other hand, traffic patterns consist of many spikes that are short in duration, you may want to specify a shorter period of time; doing so assigns less weight to the short spikes.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300. The default value is 15 seconds.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and the maximum number of channels your Pipeline supports. The default setting is 1.
Dependencies: This setting applies only to MP+ calls (Encapsulation setting is MPP). For optimum MP+ performance, both sides of a connection must set these settings to the same values:
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and the maximum number of channels your Pipeline supports.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
When utilization exceeds the threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. Using the Add Time and Sub Time settings prevents the system from continually adding and subtracting bandwidth, and can slow down the process of allocating or removing bandwidth.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300.
When the Pipeline is using MP+ (Encapsulation setting is MPP), the default value is 5.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
When utilization falls below the threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel. Using the Add Time and Sub Time settings prevents the system from continually adding and subtracting bandwidth, and can slow down the process of allocating or removing bandwidth.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300.
When the Pipeline is using MP+ (Encapsulation setting is MPP), the default value is 10.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 65535. If you specify 0 (zero), Pipeline does not enforce a limit; an idle connection stays open indefinitely.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
This setting specifies the target percentage of bandwidth utilization for an MP+ call (Encapsulation setting is MPP).
The Pipeline uses the historical time period specified by the Sample Time setting as the basis for calculating average line utilization (ALU) of transmitted data. It then compares ALU to the amount specified in the Target % setting.
When ALU exceeds the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. When ALU falls below the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel.
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 100.
The default is 70. When the value is 70%, the device adds bandwidth when it exceeds a 70 percent utilization rate, and subtracts bandwidth when it falls below that number.
Dependencies: When selecting a target utilization value, keep these guidelines in mind:
For example, an application might be able to use 88% of a 64-Kbps link, but only 70% of a 256-Kbps link.
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 99. The default value is 0; this setting causes the Pipeline to ignore bandwidth utilization when determining whether to clear a call.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
By default, any packet destined for the WAN causes the Pipeline to place a call. In addition, by default, every packet resets the idle timer, the indicator that the Pipeline uses to know when to clear a call. When you set up a Call Placement Filter, only those packets that the Call Placement Filter forwards can initiate a call or reset the Preempt or Idle Timeout settings.
Usage: Click the Call Placement Filter button. In the window that appears, select a filter or None and then click OK.
If you select None, the Pipeline forwards all packets. None is the default.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Usage: Check this box to make the filter or firewall assigned to this Connection Profile persist after the connection has been torn down.