 |
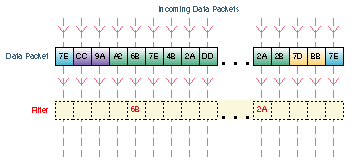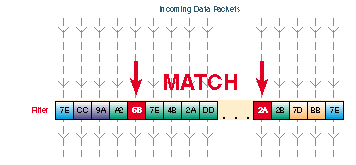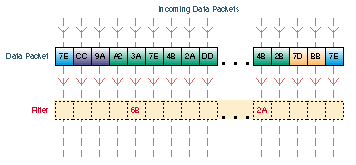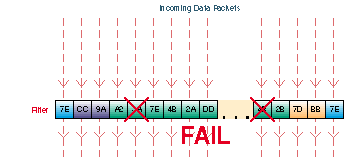
Filters -- Filters can be created for the Pipeline products to customize operation with specific types of packets or packet addresses. Filters can be used to restrict access to or from defined destinations, or to identify which packets will cause a connection (call) to be made. Filter conditions can be set up to cover a wide variety of different requirements and restrictions.
Filters are setup in the Filters tab. Filters look for certain values in defined segments of a packet. The filter checks each packet that comes into the Pipeline from the WAN, or it checks each packet that leaves the Pipeline from the LAN or PC. If a packet if found that matches the value in the filter, the packet is either discarded or allowed to continue to its destination (or further checked by another filter), depending the rules setup in the filter. In the illustration above, packets with a matching value at the designated segment are discarded.
The illustration below shows a portion of a UDP packet. The UDP header segment is an 8-byte segment (the detail is not shown here) containing a 16-bit application source port, followed by a 16-bit application destination port, plus other information about packet length, checksums, and the UDP data. If you wanted to filter out packets whose application source port or destination port is an FTP service, you would discard packets whose source or destination port is equal to 21.

The following table shows the value for common
network applications:
FTP-DATA
File Transfer Data FTP
File Transfer Control TELNET
Terminal Services SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol NAMESERV
Host Name Server NICKNAME
Who is DOMAIN
Domain Name Server TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol FINGER
Finger SNMP
SNMP Net Monitor SNMP-TRAP
SNMP Traps SYSLOG
Syslog RIP
UDP Routing Info Protocol