Compression
Description:
This setting turns data compression on or off for a PPP link.
- None
- This turns off data compression.
- Stac
- This turns on data compression.
The Pipeline applies the STACKER LZS compression/decompression algorithm. STAC is the default.
This turns on Microsoft LZS Coherency Compression for Windows95, a proprietary compression scheme for Windows 95 only (not for Windows NT).
- Stacker LZS Compression (as defined in the Internet Draft of November 1995) and Microsoft LZS Coherency Compression for Windows 95 both use the same PPP option to indicate that their compression scheme is in use. Therefore, a router can have difficulty determining exactly which compression method a caller is requesting. Ascend units handle this ambiguity in the call by always using the compression scheme specified in the Connection Profile; if there is no Connection Profile, the Ascend unit uses the compression scheme specified in the Answer tab.
- Both sides of the link must set Compression to Stac or Microsoft Stac to turn on data compression.
- The Compression setting applies only if the link uses PPP encapsulation (Encapsulation setting is PPP or MPP).
- Compression in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Compression setting takes precedence.
Data Filter
Description: This button lets you specify a data filter to use for incoming calls. This data filter examines each incoming or outgoing packet on a WAN, and either forwards or discards it.Usage: Click the Data Filter button. In the window that appears, select a data filter and then click OK.
If you choose None, the Pipeline forwards all data packets. None is the default.
Dependencies:
Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Pipeline applies a Call Placement Filter after applying a data filter; only those packets that the data filter forwards can reach the Call Placement Filter.
- If IPX client bridging is in use (Discard RIP, SAP setting is Client), set Data Filter to None.
- Do not confuse this Data Filter setting with the Data Filter setting in the Connections tab.
- This Data Filter setting applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Data Filter setting takes precedence.
- If the Require Connection Profile setting is checked in the Answer tab, Data Filter does not apply (Data Filter setting is dimmed) in the Answer tab.
Group
Description: This setting points to nailed-up channels used by the WAN link.Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 3.
Example: If Call Type is Nailed/MPP in a Connection Profile, the setting 3 assigns one nailed-up group to the profile.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Group setting does not apply (Group is dimmed) if the link consists entirely of switched channels (Call Type is Switched).
- If you add channels to the Group setting and save your changes, the Pipeline adds the additional setting to any online connection that uses the group.
- Do not assign more than one active Connection Profile to a group.
- Do not assign a Connection Profile to a group that a Frame Relay Profile uses.
- If you are using an ISDN BRI line the Pipeline assigns the B channels to the following groups:
Dial In/Out
Description: This setting specifies whether the Pipeline can initiate calls, receive them, or both. The setting you choose affects calls to or from the destination specified by the Station and IP Address settings in the Connection Profile.Usage: Choose one of the following:
- Dial In Only
- This specifies that the Pipeline can receive calls from the destination specified in the Connection Profile, but cannot initiate calls to that destination.
- Dial Out Only
- This specifies that the Pipeline can dial out to the destination specified in the Connection Profile, but cannot answer calls from that destination.
- Both
- This specifies that the Pipeline can initiate calls to the destination specified in the Connection Profile, and that it can receive calls from that destination as well.
Encapsulation
Description: This setting enables you to choose the encapsulation method to use when exchanging data with a remote network.Usage: Choose one of the following:
- MPP
- PPP
- MP
- Frame Relay
-
MP+ (Multilink Protocol Plus) extends the capabilities of MP (Multilink PPP) to support inverse multiplexing, session management, and bandwidth management. MP is an extension of PPP that supports the ordering of data packets across multiple channels.
MP+ consists of two components: a low-level channel identification, error monitoring, and error recovery mechanism, and a session management level for supporting bandwidth modifications and diagnostics. MP+ enables the Pipeline to perform Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA)-that is, MP+ enables the Pipeline to add or remove channels without disconnecting a link as the need for bandwidth increases or decreases.
Both the dialing side and the answering side of the link must support MP+. If only one side supports MP+, the connection then tries to use MP. If that fails, the connection uses standard single-channel PPP. Note that neither MP nor PPP support DBA.
-
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) provides a standard means of encapsulating data packets over a single-channel WAN link that a Connection Profile sets up. It ensures basic compatibility with non-Ascend devices.
For this setting to work, both the dialing side and the answering side of the link must support PPP.
-
Frame Relay is an HDLC-based packet protocol that enables you to send data to a destination using one or more frame relay switches within a private network or a public carrier's network. HDLC stands for High Level Data Link Control.
From the viewpoint of the Pipeline, a frame relay switch is an endpoint for all DLCIs (Data Link Connection Indicators) connecting to it. A DLCI identifies a Connection Profile as a logical link. The frame relay switch connects the endpoints of the DLCIs to each other to make a virtual permanent circuit to which users can connect. The circuit acts like a wire between two endpoints with a fixed maximum bandwidth.
- The Encapsulation setting does not apply (Encapsulation setting is dimmed) when the Pipeline answers a call, or if the link consists of only nailed-up channels (Call Type setting is Nailed).
- If the Call Type setting is Nailed/MPP then Encapsulation must be set to MPP. In this case, or whenever the Encapsulation setting is MPP, the Pipeline adds or subtracts switched channels on the connection as required by the DBA settings on either side of the connection.
- If the Encapsulation setting is MPP and the Call Type setting is Nailed/MPP, the minimum number of channels in the link is the number set by Min Channels or the number of nailed-up channels in the group, whichever is greater.
- If the Encapsulation setting is MPP and the Call Type setting is Nailed/MPP, the maximum number of channels in the link is the number set by Max Channels or the number of nailed-up channels in the group, whichever is greater.
Max PPP Packet Size
Description: This setting specifies the maximum number of bytes the Pipeline can receive in a single packet on a PPP link. MRU stands for Maximum Receive Unit.Usage: The default setting is 1524; you should accept this default unless the device at the remote end of the link cannot support it.
If the administrator of the remote network specifies that you must change this value, enter a number between 1 and 1524.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Max PPP Packet setting applies to any link using PPP encapsulation (Encapsulation setting is MPP, MP, or PPP).
- Max PPP Packet Size in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Max PPP Packet Size setting takes precedence.
- If Require Connection Profile setting is checked in the Answer tab, Max PPP Packet Size does not apply (Max PPP Packet Size setting is dimmed) in the Answer tab.
Dial-In Settings
Password
Description: This setting specifies the password that the Pipeline requires when receiving a call for this connection profile.Usage: Enter the password.
You can enter up to 20 characters; the password is case sensitive. Leave the field blank if the remote end does not require a password.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The far end must specify a value for Password when the link uses PPP encapsulation (Encapsulation setting is PPP or Encapsulation setting is MPP) and the Pipeline uses PAP, CHAP, or Cache-Token authentication (Authentication setting is PAP, Authentication setting is CHAP, or Authentication setting is Cache-Token).
Force Callback
Description: This setting enables or disables the callback feature.When you enable the callback feature, the Pipeline hangs up after receiving an incoming call that matches the one specified in the Connection Profile. The Pipeline then calls back the device at the remote end of the link using the Number setting specified in the Connection Profile.
You can use this setting to tighten security, as it ensures that the Pipeline always makes a connection with a known destination.
Usage: Check this to enable the callback feature.
By default, this is not checked.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Force Callback setting does not apply (Force Callback setting is dimmed) if all channels of the link are nailed up (Call Type setting is Nailed).
- If Force Callback is checked, you must also set Dial In/Out to Both, because the Connection Profile must both answer the call and call back the device requesting access.
Request Link Monitoring (LQM)
Description: This setting specifies whether the Pipeline requests Link Quality Monitoring (LQM) when answering a PPP call.LQM is a feature that enables the Pipeline to monitor the quality of a link. LQM counts the number of packets sent across the link and periodically asks the remote end how many packets it has received. Discrepancies are evidence of packet loss and indicate link quality problems.
LQM causes the generation of periodic link quality reports. Both ends of the link exchange these reports.
Usage:
- If the checkbox is checked, the Pipeline requests LQM.
- If the checkbox is not checked, the Pipeline does not request LQM.
- Both sides of the link negotiate the interval between periodic link quality reports; however, the interval must fall between the minimum interval (as set by Minimum LQM) and the maximum interval (as set by Maximum LQM).
- If LQM is turned off (Request Link Monitoring (LQM) setting is unchecked), the Maximum LQM and Minimum LQM settings do not apply (Maximum LQM setting is dimmed and Minimum LQM setting is dimmed).
- LQM applies only if the Encapsulation setting is PPP.
- Request Link Monitoring (LQM) in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Request Link Monitoring (LQM) setting takes precedence.
Minimum LQM
Description: This setting specifies the minimum duration between link quality reports, measured in tenths of a second.Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 600. The default is 600.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- If the Request Link Monitoring (LQM) setting is unchecked, the Minimum LQM setting does not apply (Minimum LQM setting is dimmed).
- Minimum LQM in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the Minimum LQM setting in the Connection Profile takes precedence.
Maximum LQM
Description: This setting specifies the maximum duration between link quality reports, measured in tenths of a second.Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 600. The default is 600.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- If the Request Link Monitoring (LQM) setting is unchecked, the Maximum LQM setting does not apply (Maximum LQM setting is dimmed).
- Maximum LQM in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the Maximum LQM setting in the Connection Profile takes precedence.
Number
Description: The Number setting specifies the phone number the Pipeline dials to reach the remote network.Usage: Enter a telephone number. You can enter up to 37 characters, and you must limit those characters to the following:
1234567890()[]!z-*#|The Pipeline sends only the numerical characters to place a call.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Dial On Broadcast
Description: This setting specifies whether broadcast packets initiate dialing.Usage:
- If the checkbox is checked, the Pipeline dials a link if (a) the link is not online and (b) the Pipeline receives a frame whose MAC address is set to broadcast.
- If the checkbox is unchecked, broadcast packets do not initiate dialing.
This is unchecked by default.
Bill-to Number
Description: This setting specifies a billing number for charges incurred on the line. If you do not enter a billing number, the telephone company bills charges the telephone number assigned to the line.
- Your carrier determines the billing number, and uses it to sort your bill. If you have several departments, and each department has its own Bill-to Number, your carrier can separate and tally each department's usage.
Usage: Enter the telephone number to be billed. You can specify up to ten characters, and you must limit those characters to the following:
1234567890()[]!z-*# |Dependencies: Bill-to Number for outgoing calls on an ISDN BRI line applies only to installations in Australia.
Authentication
Description:
This setting specifies the authentication protocol that the Pipeline requests when initiating a connection using PPP or MP+ encapsulation. The answering side of the connection determines which authentication protocol, if any, the connection uses.
- None
- This specifies that the Pipeline does not request an authentication protocol for outgoing calls.
None is the default.
- This is a PPP authentication protocol.
If you choose PAP, the Pipeline requests this protocol for authentication. The remote device must support PAP.
Note that if you choose this setting, the Pipeline requests PAP authentication but will use CHAP authentication if the called unit requires CHAP. Choose this setting for non-token card authentication if you would allow sending your password unencrypted.
- This is a PPP authentication protocol. If you choose CHAP, the Pipeline requests this protocol for authentication. The remote device must support CHAP.
Note that if you choose this setting, the Pipeline will not bring up the connection using PAP. Choose this setting for non-token card authentication if you do not wish to send your password unencrypted; that is, if you do not wish to be authenticated through PAP.
- This is an extension of PAP authentication. It requires the following:
- The Network Access Server (NAS) must be running the Ascend RADIUS daemon.
-
In PAP-Token, the user making outgoing calls from the Pipeline authenticates his or her identity by entering a password derived from a hardware device, such as a hand-held security card. The Pipeline prompts the user for this password, possibly along with a challenge key. The NAS obtains the challenge key from a security server that it accesses through RADIUS.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) is a protocol by which users can have access to secure networks through a centrally managed server. You can store virtually all Connection Profile information on the RADIUS server in a flat ASCII database.
- This is nearly identical to PAP-Token. It requires the following:
- the NAS be running the Ascend RADIUS daemon
Note: If MPP Password and Ascend-Receive-Secret do not match, it does not prevent the initial connection from succeeding, but the Pipeline cannot extend an MP+ call beyond a single channel.
- The link must use PPP or MP+ encapsulation (Encapsulation setting is PPP or Encapsulation setting is MPP).
- If you request PAP or CHAP, you must also specify a password using Password in a Connection Profile.
- On a nailed-up link (Call Type setting is Nailed), you must set Authentication to the same value at both ends of the connection; that is, Authentication at the local and remote ends must all contain the same value.
- PAP-Token and PAP-Token-CHAP require configuration of a SAFEWORD or ACE entry in the NAS's RADIUS users file with the caller's name.
- For information on prompting for a password at a host, see the APP Server, APP Host, and APP Port settings.
- Dial on Broadcast must be enabled when a PC on the same Ethernet as the Pipeline runs APPSRVR1 or APPSRVR2 to open a connection protected by security-card authentication.
Password
Description: This setting specifies the password that the Pipeline sends to the remote device.Usage: Enter a password. You can enter up to 20 characters; the password is case sensitive. The default is null.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- If the Authentication setting is None, the Password setting does not apply (Password setting is dimmed).
- You must specify a value for Password when the link uses PPP encapsulation (Encapsulation setting is PPP or MPP) and the Pipeline uses either PAP or CHAP authentication (Authentication setting is PAP or CHAP).
MPP Password
Description: This setting specifies the password that the Pipeline sends when it adds channels to a security-card MP+ call that uses PAP-Token-CHAP authentication. The Pipeline obtains authentication of the first channel of this MP+ call from the hand-held security card.Usage: Enter a password. This password must match the one set up for your Pipeline in the RADIUS users file on the NAS (Network Access Server).
Dependencies: MPP Password applies only to outgoing MP+ calls in which the Authentication setting is PAP-Token-CHAP.
Call Placement Filter
Description: This setting lets you specify a Call Placement Filter to plug into a Connection Profile.By default, any packet destined for the WAN causes the Pipeline to place a call. In addition, by default, every packet resets the idle timer, the indicator that the Pipeline uses to know when to clear a call. When you set up a Call Placement Filter, only those packets that the Call Placement Filter forwards can initiate a call or reset the Preempt or Idle Timeout settings.
Usage: Click the Call Placement Filter button. In the window that appears, select a filter and then click OK.
If you choose None, the Pipeline forwards all data packets. None is the default.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- If all channels of a link are nailed up (Call Type setting is Nailed in the Connection Profile), the Call Placement Filter setting does not apply (Call Placement Filter setting is dimmed).
- The Pipeline applies a Call Placement Filter after applying a data filter; only those packets that the data filter forwards can reach the Call Placement Filter.
- If IPX client bridging is in use (Discard RIP, SAP setting is Broadcasts), set the Call Placement Filter setting to None.
- Call Placement Filter in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Call Placement Filter setting takes precedence.
- If the Require Connection Profile setting is checked in the Answer tab, Call Placement Filter does not apply (Call Placement Filter setting is dimmed) in the Answer tab.
IP Options settings
IP Address
Description: This setting specifies the IP address of a station or router at the remote end of the link specified by the Connection Profile.Usage: Enter the IP address of a remote station or router.
An IP address consists of four numbers between 0 and 255, separated by periods.
The default setting is 0.0.0.0; an answering Connection Profile with this setting matches all incoming IP addresses.
Example:
200.207.23.101
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The IP Address setting in the first Connection Profile is the same as the IP Address setting in the Configure Profile.
- The value of the IP Address setting on the local Pipeline must match the IP Address setting of the unit at the remote end of the link.
- No two calling Connection Profiles should have the same IP Address.
- Setting IP Address to 0.0.0.0 and clearing the Station setting resets all settings in the Connection Profile to their defaults.
- The IP Address setting does not apply (IP Address setting is dimmed) if the Pipeline does not support IP (Route IP setting is unchecked).
- If you do not know the right IP address to enter, you must obtain it from the network administrator.
Private Address
Description: The Private Address setting specifies whether the Pipeline discloses the IP address indicated by IP Address when queried by RIP (Routing Information Protocol) or another routing protocol.Usage:
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
Subnet Mask
Description: This setting specifies the subnet containing the IP address for the Pipeline.Usage: Click the up arrow to add bits to the subnet mask. Click the down arrow to take away bits from the subnet mask. The mask and the number of bits in the mask are shown to the right of the arrows.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The value of the Subnet Mask setting must match the Subnet Mask setting expected by the device to which the Pipeline connects.
- If you do not know the right subnet mask to enter, you must obtain it from the network administrator. Do not attempt to configure the subnet mask by guesswork!
WAN Alias
Description: This setting specifies the IP address of the link's remote interface to the WAN.
The WAN Alias setting applies only if the remote end of a link uses an implementation of PPP that requires that both ends of a WAN connection be on the same subnet.
200.207.23.7/24
Interface Address
Description:
This setting specifies the IP address of the interface at the near end of a link. 200.207.23.7/24
Subnet Mask
Description:
This setting specifies the subnet containing the IP address specified by the Interface Address setting.
Usage: Click the up arrow to add bits to the subnet mask. Click the down arrow to take away bits from the subnet mask. The mask and the number of bits in the mask are shown to the right of the arrows.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The value of the Subnet Mask setting must match the Subnet Mask setting expected by the device to which the Pipeline connects.
- If you do not know the right subnet mask to enter, you must obtain it from the network administrator. Do not attempt to configure the subnet mask by guesswork!
Virtual Hops
Description: The Virtual Hops setting determines the virtual hop count of the link.If there are two routes available to a single destination network, you can ensure that the Pipeline uses any available nailed-up channel before using a switched channel by setting the Virtual Hops setting to a value higher than the metric of any nailed-up route. The higher the value entered, the less likely that the Pipeline will bring the link or route online. The Pipeline uses the lowest metric.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 15. This value is the virtual hop count. The default setting is 7.
Example: If a route to a station takes three hops over nailed-up lines, and the Virtual Hops setting is 4 in a Connection Profile that reaches the same station, the Pipeline does not bring the Connection Profile's link online.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Virtual Hops setting in a Connection Profile does not apply to bridged connections.
- If you enable RIP (Routing Information Protocol) across the WAN in a Connection Profile or an Answer tab, the hop count for the route can differ from the value of the Virtual Hops setting in the Route Profile because the Pipeline always uses the lower hop count.
- The hop count includes the metric of each switched link in the route.
- Virtual Hops only applies to IP connections.
Priority
Description: This setting specifies the preference value for a static IP route configured in a Connection Profile.When choosing which routes to put in the routing table, the router first compares the Priority values, preferring the lower number. If the Priority values are equal, the router compares the Virtual Hops setting values, using the route with the lower number of hops.
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 255. The value of 255 means "Don't use this route"; this value is meaningful only for Connection Profiles.
Dependencies: These are the default values for different types of routes:
- The Routes learned from OSPF setting is 10.
- The Routes learned from ICMP Redirects setting is 30.
- The Routes learned from RIP setting is 100.
Compress IP Header
Description: This checkbox turns Van Jacobson (VJ) TCP/IP header compression on or off.Usage: If checked, header compression is enabled.
Checked is the default. The Ascend unit must include the optional compression module. Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- This setting applies only to packets in TCP applications, such as Telnet.
Bandwidth settings
DBA Monitor
Description: This setting specifies how the Pipeline monitors the traffic over a Multilink Protocol Plus (MPP) call.Usage: Choose one of the following:
Dependencies: DBA Monitor is only supported on MPP calls (Encapsulation setting is MPP).
DBA Algorithm
Description: This setting specifies which Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) algorithm to use for calculating average line utilization (ALU) of transmitted data. DBA enables you to specify that the Pipeline uses ALU as the basis for automatically adding or subtracting bandwidth from a switched connection without terminating the link.The Pipeline uses the historical time period specified by the Sample Time setting as the basis for calculating ALU. It then compares ALU to the amount specified in the Target % setting. When ALU exceeds the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. When ALU falls below the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel.
MP+ supports Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation.
Usage: Choose one of the following:
- Constant
- This gives equal weight to all samples taken during the historical time period specified by the Sample Time setting.
When you select this, older historical samples have as much impact on the decision to change bandwidth allocation as do more recent samples.
- This gives more weight to recent samples of bandwidth usage than to older samples taken during the historical period specified by the Sample Time setting; the weighting grows at a linear rate.
- This gives more weight to recent samples of bandwidth usage than to older samples taken during the historical period specified by the Sample Time setting; the weighting grows at a quadratic rate.
This graph illustrates the results of each algorithm:
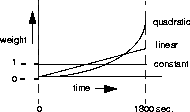
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- To dynamically allocate bandwidth by tracking line usage, you use the Add Time, DBA Algorithm, Max Channels, Min Channels, Sample Time, Sub Time, and Target % settings.
- DBA Algorithm in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, its DBA Algorithm setting takes precedence.
Sample Time
Description: This setting specifies the number of seconds the Pipeline uses as a sample for calculating average line utilization (ALU) of transmitted data; the Pipeline arrives at this average using the algorithm specified by the DBA Algorithm setting.When ALU exceeds the Target % threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel.When ALU falls below the Target % threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel.
The number of seconds you choose for the Sample Time setting depends on your device's traffic patterns. For example, if you want to average spikes with normal traffic flow, you may want the Pipeline to establish a longer historical time period. If, on the other hand, traffic patterns consist of many spikes that are short in duration, you may want to specify a shorter period of time; doing so assigns less weight to the short spikes.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300. The default value is 15 seconds.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Sample Time setting applies only to dynamic MP+ calls (Encapsulation setting is MPP).
- If you specify a small value for the Sample Time setting, and increase the values of the Add Time setting and the Sub Time setting relative to the value of Sample Time, the system becomes less responsive to quick spikes.
- The easiest way to determine the proper values for Sample Time, Add Time, and Sub Time is to observe usage patterns; if the system is not responsive enough, the value of Sample Time is too high.
Base Channels
Description: This setting specifies the initial number of channels the Pipeline sets up when originating calls for a PPP, MP+, or MP multichannel link.Usage: Enter a number between 1 and the maximum number of channels your system supports. The default setting is 1.
The maximum value of the Base Channels setting depends on the encapsulation method that both ends of the link use.
- For an PPP link (for which Encapsulation setting is PPP), the value of Base Channels is always 1.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- You can determine the base bandwidth of a call by multiplying the value of the Base Channels setting by the value of the Link Type setting.
- The Base Channels setting does not apply (Base Channels setting is dimmed) when all channels of the link are nailed up (Call Type setting is Nailed).
- For optimum MP+ performance, both sides of a connection must set these settings to the same values:
- Base Channels
- Min Channels
- Max Channels
Min Channels
Description: This setting specifies the minimum number of channels an MP+ call maintains.Usage: Enter a number between 1 and the maximum number of channels your system supports. The default setting is 1.
Dependencies: The Min Channels setting applies only to MP+ calls (Encapsulation setting is MPP). For optimum MP+ performance, both sides of a connection must set these settings to the same values:
Max Channels
Description: This specifies the maximum number of channels allowed on an MP+ call.Usage: Enter a number between 1 and the maximum number of channels your system supports.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- The Max Channels setting applies only to dynamic MP+ calls (Encapsulation setting is MPP).
- For optimum MP+ performance, both sides of a connection must set these settings to the same values:
- Base Channels
- Min Channels
- Max Channels
Add Time
Description: This setting specifies the number of seconds that average line utilization (ALU) for transmitted data must exceed the threshold indicated by the Target % setting before the Pipeline begins adding bandwidth to a session. The Pipeline determines the ALU for a session by using the algorithm specified by the DBA Algorithm setting.When utilization exceeds the threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. Using the Add Time and Sub Time settings prevents the system from continually adding and subtracting bandwidth, and can slow down the process of allocating or removing bandwidth.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300.
When the Pipeline is using MP+ (Encapsulation setting is MPP), the default value is 5.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- Additional channels must be available, and the number of channels added cannot exceed the amount specified by the Max Channels setting.
- Add Time in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Add Time setting takes precedence.
- If Require Connection Profile setting is checked in the Answer tab, Add Time does not apply (Add Time setting is dimmed) in the Answer tab.
- Add Time and Sub Time have little or no effect on a system with a high Sample Time value.
Sub Time
Description: This setting specifies the number of seconds average line utilization (ALU) of transmitted data must fall below the threshold indicated by the Target % setting before the Pipeline begins removing bandwidth from a session. The Pipeline determines the ALU for a session using the algorithm specified by the DBA Algorithm setting.When utilization falls below the threshold for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel. Using the Add Time and Sub Time settings prevents the system from continually adding and subtracting bandwidth, and can slow down the process of allocating or removing bandwidth.
Usage: Enter a number between 1 and 300.
When the Pipeline is using MP+ (Encapsulation setting is MPP), the default value is 10.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- One channel must be up at all times.
- Removing bandwidth cannot (a) cause the ALU to exceed the threshold specified by the Target % setting or (b) cause the number of channels to fall below the amount specified by the Min Channels setting.
- Sub Time in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Sub Time setting takes precedence.
- Add Time and Sub Time have little or no effect on a system with a high Sample Time value.
Idle Preempt Time
Description: This setting specifies the number of seconds the Pipeline waits before ending a call when the ISDN line is not being used.Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 65535. If you specify 0 (zero), the Pipeline does not enforce a limit; an idle connection stays open indefinitely.
Target %
Description: The Target % setting specifies the percent bandwidth utilization at which the Pipeline adds or subtracts bandwidth dynamically.This setting specifies the target percentage of bandwidth utilization for an MP+ call (Encapsulation setting is MPP).
The Pipeline uses the historical time period specified by the Sample Time setting as the basis for calculating average line utilization (ALU) of transmitted data. It then compares ALU to the amount specified in the Target % setting.
When ALU exceeds the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Add Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to add a channel. When ALU falls below the threshold defined by Target % for a period of time greater than the value of the Sub Time setting, the Pipeline attempts to remove a channel.
Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 100.
The default is 70. When the value is 70%, the device adds bandwidth when it exceeds a 70 percent utilization rate, and subtracts bandwidth when it falls below that number.
Dependencies: When selecting a target utilization value, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Monitor how the application behaves when using different bandwidths.
- Monitor the application at different loads.
Idle %
Description: This setting specifies a percentage of bandwidth utilization below which the Pipeline clears a single-channel MP+ call. Bandwidth utilization must fall below this percentage on both sides of the connection before the Pipeline clears the call.Usage: Enter a number between 0 and 99. The default value is 0; this setting causes the Pipeline to ignore bandwidth utilization when determining whether to clear a call.
Dependencies: Keep this additional information in mind:
- MP+ must be the selected encapsulation method (Encapsulation setting is MPP) in a Connection Profile.
- If the device at the remote end of the link enters an Idle % setting lower than the value you specify, the Pipeline does not clear the call until bandwidth utilization falls below the lower percentage.
- If either end of a connection sets the Idle % setting to 0 (zero), the Pipeline ignores bandwidth utilization when determining when to clear a call.
- If the time set by the Idle Timeout setting expires, the call disconnects whether or not bandwidth utilization falls below the Idle % setting.
- When bandwidth utilization falls below the Idle % setting, the call disconnects regardless of whether the time specified by the Idle Timeout setting has expired.
- Because the Idle % setting is dependent on traffic levels on both sides of the connection, we recommend that you use the Idle Timeout setting in preference to it.
- Idle % in the Answer tab applies to incoming calls for which no Connection Profile exists; if a Connection Profile exists, the setting of its Idle % setting takes precedence.
- If Require Connection Profile setting is checked in the Answer tab, Idle % does not apply (Idle Timeout setting is dimmed) in the Answer tab.
Filters Are Persistent
Description: This setting specifies whether the filter or firewall assigned to a Connection Profile should persist after the call has been disconnected.Usage: Check the box to make the filter persistent.
- If checked, the filter or firewall assigned to this Connection Profile will persist after the connection has been torn down.
Note: Typically a firewall will persist for about an hour after its associated connection has been torn down.
Backup Connection
Description:
This setting specifies a backup connection.
Secondary Connection
Description:
This setting specifies a secondary Connection Profile to be dialed in the event that a session using the primary Connection Profile cannot be established.
- Secondary Connection Profiles cannot be nested. That is, secondary Connection Profiles cannot also have Secondary Connection profiles.
- Do not confuse the Secondary Connection setting with the Backup Connection setting. A Backup Connection setting is used to re-establish an existing connection that has terminated; a Secondary Connection setting is used to establish a new connection if the primary Connection Profile cannot.
- Settings that you define in the primary Connection Profile do not automatically apply to the secondary Connection Profile.
- Outgoing Frame Relay packets are the only packets that follow the primary Connection Profile definitions. All other packets follow the backup Connection Profile definitions.